# 你不知道的 JSON.stringify 特性

# 前言
;JSON.stringify可配合JSON.parse来进行对象深拷贝,也可以用于字符串转换为对象,但是会有很多问题。
# 语法特性
;JSON.stringify (opens new window) 用于将JavaScript对象或值转换为JSON字符串。
# undefined、函数、Symbol
# 作为对象属性值
;undefined、函数或者Symbol在序列化时会被忽略,换句话说会丢失掉。
const object = {
foo: undefined,
bar: function () {
console.log(this)
},
baz: Symbol('baz'),
id: 1
}
JSON.stringify(object) // {"id":1}
# 作为数组元素
作为数组元素,将序列化为null。
const array = [undefined, function () { }, Symbol('foo'), 'bar']
JSON.stringify(array) // [null,null,null,"bar"]
# 单独序列化
单独序列化,将返回undefined。
JSON.stringify(undefined) // undefined
JSON.stringify(function () { }) // undefined
JSON.stringify(Symbol('foo')) // undefined
# null、Infinity、NaN
;NaN和Infinity格式的数值或者null,序列化时都将转换为null。
JSON.stringify({ foo: NaN, id: 1 }) // {"foo":null,"id":1}
JSON.stringify([null, Infinity, NaN]) // [null,null,null]
JSON.stringify(NaN) // null
JSON.stringify(2E+10308) // null
# 包装对象
布尔、数值或者字符串的包装对象,在序列化时会转换为对应的原始值。
JSON.stringify({ foo: new String('foo'), bar: new Number(123), baz: new Boolean(true) }) // {"foo":"foo","bar":123,"baz":true}
JSON.stringify([new String('foo'), new Number(123), new Boolean(true)]) // ["foo",123,true]
JSON.stringify(new String('foo')) // "foo"
# 序列化顺序
非数组对象的属性,无法保证在序列化后的字符串中的出现顺序。
JSON.stringify({ foo: 'foo', 3: 'bar', 1: 'baz' })) // {"1":"baz","3":"bar","foo":"foo"}
# toJSON
若序列化的对象包含toJSON方法,则将对toJSON方法的返回值执行序列化。
const array = [1, 2, 3]
array.toJSON = () => 'hello'
JSON.stringify(array) // "hello"
JSON.stringify({
bar: 'bar',
foo: {
toJSON() {
return NaN
}
}
}) // {"bar":"bar","foo":null}
;Date对象部署了toJSON方法,序列化时会被调用。
const date = new Date()
date.toJSON() // 2022-01-04T03:32:23.852Z
JSON.stringify(date) // "2022-01-04T03:32:23.852Z"
# 枚举属性
序列化对象时,仅仅序列化可枚举的属性。
const object = {}
Object.defineProperties(object, {
foo: {
value: 'foo',
enumerable: false
},
bar: {
value: 'bar',
enumerable: true
}
}) // {bar: "bar", foo: "foo"}
JSON.stringify(object) // {"bar":"bar"}
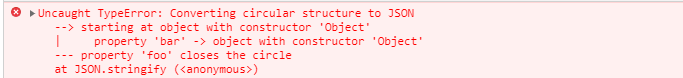
# 循环引用
循环引用的对象,序列化时,会抛出错误。
const foo = {}
const bar = {
foo
}
foo.bar = bar
JSON.stringify(foo)
# Symbol 属性
以Symbol作为属性键时会被忽略掉,即使在replacer参数中强制指定了。
const object = {
bar: 'bar',
[Symbol('foo')]: 'foo'
}
JSON.stringify(object, (k, v) => {
if (typeof k === 'symbol') {
return v
}
return v
}) // {"bar":"bar"}
# 正则、错误对象
正则表达式或者错误对象,序列化过程中会被转换为空对象。
const object = {
bar: 'bar',
reg: /a+/,
err: new Error('err')
}
JSON.stringify(object) // {"bar":"bar","reg":{},"err":{}}
# 原型链
若对象中的键值为某个构造函数的实例,序列化后将重置对象的constructor为Object。
function Person(key) {
this.key = key
}
const object = {
id: 1,
foo: new Person('foo')
}
const copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(object))
object.foo.constructor // ƒ Person(key) { this.key = key }
copy.foo.constructor // ƒ Object() { [native code] }
# 参数
# 第二个参数 replacer
第二个参数可以为函数,也可以为数组。
作为数组时,只有数组内的属性名才会被序列化。
const object = {
id: 1,
foo: 'foo',
bar: 'bar',
baz: 'baz'
}
JSON.stringify(object, ['id', 'foo']) // {"id":1,"foo":"foo"}
作为函数时,函数包括两个参数,分别为键key和值value。但是第一次时,键key为空字符串,值value为被stringify的对象。
const object = {
id: 1,
foo: 'foo',
}
JSON.stringify(object, (key, value) => {
console.log(key, '/', value)
return value
})
// / {id: 1, key: "foo"}
// id / 1
// key / foo
# 第三个参数 space
第三个参数用于控制结果中字符串的间距,美化输出。
const object = {
id: 1,
key: 'foo',
}
JSON.stringify(object, undefined, 2)
// {
// "id": 1,
// "key": "foo"
// }
# JSON.parse
;JSON.parse (opens new window) 用于解析JSON字符串为JavaScript的值或对象。
JSON.parse('{}') // {}
JSON.parse('true') // true
JSON.parse('[1, "foo"]') // [1, "foo"]
JSON.parse('null') // null
第二个可选参数reviver函数,也包括两个参数,分别为键key和值value。解析顺序是由内向外,最后一次时,键key为空字符串,值value为当前的解析值。
const stringify = '{"id":1,"model":{"bar":"baz"},"list":["foo"]}'
JSON.parse(stringify, (key, value) => {
console.log(key, '/', value)
return value
})
// id / 1
// bar / baz
// model / {bar: "baz"}
// 0 / foo
// list / ["foo"]
// / {id: 1, model: {…}, list: Array(1)}
数组也是对象,特殊性在于索引相当于键
# 常见问题
# 如何序列化 ES6 的 Map 类型
与正则和错误对象一致,Map类型在序列化时,将转换为空对象。
const object = {
id: 1,
map: new Map([['id', 1], ['value', 'foo']])
}
JSON.stringify(object) // {"id":1,"map":{}}
有没有可能在stringify时,将Map数据保留为数组方式呢?
当然是有的,即利用第二个参数replacer。
const replacer = (key, value) => {
if (value instanceof Map) {
return {
dataType: 'Map',
value: [...value.entries()]
}
}
return value
}
const stringify = JSON.stringify(object, replacer) // {"id":1,"map":{"dataType":"Map","value":[["id",1],["value","foo"]]}}
注意指定dataType是为了可以更好地parse恢复出原对象。
const reviver = (key, value) => {
if (typeof value === 'object' && value !== null) {
if (value.dataType === 'Map') {
return new Map(value.value)
}
}
return value
}
JSON.parse(stringify, reviver) // {id: 1, map: Map(2)}
# 小结
;JSON.stringify特性。
undefined、函数或者Symbol作为对象属性值时,将丢失掉。作为数组元素时,将返回undefined。单独序列化时,转换为nullnull、Infinity格式的数值或者NaN,将序列化为null- 布尔、数值、字符串的包装对象,在序列化时会转换为对应的原始值
- 非数组对象在序列化后无法保证属性的顺序
- 对象包含
toJSON方法,则将对toJSON方法的返回值执行序列化(Date实例就部署了toJSON方法) - 仅会序列化对象的可枚举的属性
- 循环引用的对象,序列化时会抛出错误
- 以
Symbol作为属性键时会被忽略掉 - 正则、错误对象等将会被转换为空对象
- 若对象中的键值为某个构造函数的实例,序列化后将重置对象的构造函数为
Object
# 🎉 写在最后
🍻伙伴们,如果你已经看到了这里,觉得这篇文章有帮助到你的话不妨点赞👍或 Star (opens new window) ✨支持一下哦!
手动码字,如有错误,欢迎在评论区指正💬~
你的支持就是我更新的最大动力💪~
GitHub (opens new window) / Gitee (opens new window)、GitHub Pages (opens new window)、掘金 (opens new window)、CSDN (opens new window) 同步更新,欢迎关注😉~
